Osmotic adjustment in plants
On the basis of available amount of water and salt, plants divided into three groups.
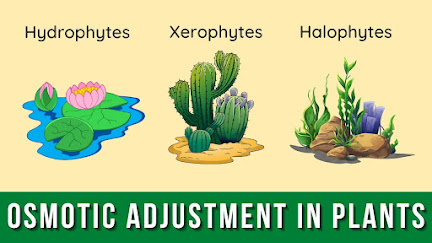
Hydrophytes:
Those plants which live partially submerge or completely in freshwater. Such plants do not face the problem of water shortage. They have developed mechanisms for the removal of extra water from their cells. Hydrophytes have broad leaves with a large number of stomata on their upper surfaces. This characteristics helps them to remove the extra amount of water.
Example:
Water lily.
Xerophytes:
They live in dry environments. They possess thick, waxy cuticle over their epidermis to reduce water loss from internal tissues. They have less number of stomata to reduce the rate of transpiration. Such plants have deep roots to absorb maximum water from soil.
Example:
Cacti (singular cactus).
Halophytes:
They live in sea water and are adapted to salty environment. Salts enter in the bodies of such plants due to their higher concentration in sea water.
Example:
Sea grass.

Halophytes plants
Previous work




.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment