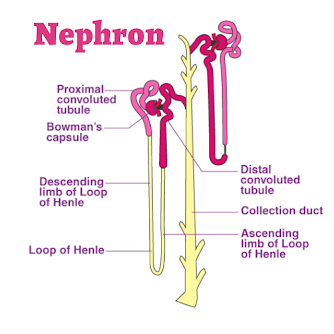
Urine
The filtrate present in renal tubules is known as urine. It moves into collecting ducts and then into pelvis.
Osmoregulatory function of kidney
Osmoregulation:
Is defined as the regulation of the concentration of the water and salt in blood and other body fluids. Kidney plays important role in osmoregulation by regulating the water fluids whereas excess intake of water dilutes them.
Hypotonic:
When there is excess water in body fluids, kidney from dilutes (Hypotonic) urine. For this purpose, kidney filter more water from glomerulus capillaries into Bowman's capsule. Similarly less water is reabsorbed and abundant dilute urine is produced. It brings down the volume of the body fluids to normal.
Hypertonic:
When there is shortage of water in body fluids, kidney filter less water from glomerulus capillaries and the rate of reabsorption of water is increased. Less filtration and more reabsorption of water produce small amount of concentration (hypertonic) urine. It increases the volume of body fluids to normal. This whole process is under hormonal control.
Previous work
Hypotonic & Hypertonic


.png)






.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)